Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ozawa, Masaki; Koyama, Shinichi; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujita, Reiko*; Mimura, Hitoshi*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.451 - 457, 2007/09
To minimize the ecological burden originating in nuclear fuel recycling, a new R&D strategy, Adv.-ORIENT (Advanced Optimization by Recycling Instructive ElemeNTs) cycle, was set forth. A key separation tool is ion exchange chromatography (IXC) by a tertiary pyridine resin having soft donor nitrogen atoms. This method has provided individual recovery of pure Am and Cm products with a Pu/U/Np fraction from irradiated fuel in just a 3-step separation. A catalytic electrolytic extraction (CEE) method by Pd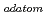 has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs
has been employed to separate, purify and fabricate RMFP catalysts. High separation efficiency of RMFP proved hydrochloric acid as a suitable media for their recovery. Different functioned ion exchangers, e.g., ammonium molybdophosphate (AMP), have been investigated for the separation of Cs . Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for
. Theoretical and laboratory studies on the isotope separation of LLFPs were begun for  Se,
Se,  Sn and
Sn and  Cs.
Cs.
Sugo, Yumi; Sasaki, Yuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Sekine, Tsutomu*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1870 - 1873, 2007/09
A tridentate diamide, 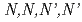 -tetraoctyldiglycolamide (TODGA) is very useful for the recovery of actinide ions from spent nuclear fuel. Based on the mechanism of the radiolysis of TODGA in organic solution, an improvement of radiolytic stability of amidic extractants was attempted. The radiolytic degradation of TODGA was suppressed by the addition of appropriate compounds, due to reduction in the mole fraction of
-tetraoctyldiglycolamide (TODGA) is very useful for the recovery of actinide ions from spent nuclear fuel. Based on the mechanism of the radiolysis of TODGA in organic solution, an improvement of radiolytic stability of amidic extractants was attempted. The radiolytic degradation of TODGA was suppressed by the addition of appropriate compounds, due to reduction in the mole fraction of  -dodecane. In addition, by using the solvents having low ionization potentials, TODGA could be protected from radiation. Because the charge transfer reaction in the primary process was inhibited. It was also confirmed that aromatic substituents in the molecule effectively improved the radiolytic stability.
-dodecane. In addition, by using the solvents having low ionization potentials, TODGA could be protected from radiation. Because the charge transfer reaction in the primary process was inhibited. It was also confirmed that aromatic substituents in the molecule effectively improved the radiolytic stability.
Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Suzuki, Kiichi; Aono, Shigenori
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.891 - 896, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Sugino, Kazuteru
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.653 - 661, 2007/09
For a validation of MAs nuclear data and improvement on the prediction accuracy of MAs transmutation properties in fast reactor cores, the MAs sample irradiation tests data of Joyo were utilized. Result of their analyses showed good agreement with experimental value, which indicates that the MAs cross sections in JENDL-3.3 are almost satisfactory for an application to fast reactor cores. Further, the present study clarified that the utilization of those data with cross section adjustment technique has the potential to reduce the uncertainty of MAs transmutation properties in fast reactor cores to less than half.
Ozawa, Takayuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.404 - 408, 2007/09
The probabilistic annular fuel design code "BORNFREE-CEPTAR" was developed for the reasonable design of annular fuels to be applied for fast reactors in future. In the probabilistic design method, the performance parameters, i.e. fuel center temperature, cladding temperature, cladding stress, etc., used to be evaluated with the Monte Carlo method under the irradiation behavior, and the quantitative design margin could be obtained. As the result of probabilistic evaluation with this code, the possibility of the improvement of reactor performance of the advanced fast reactor was quantitatively indicated.
Kato, Masato; Nakamichi, Shinya; Takano, Tatsuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.916 - 920, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Sagayama, Yutaka
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.251 - 258, 2007/09
JAEA launched a new FR Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project in cooperation with the Japanese electric utilities. The FaCT project is based on the conclusion of the Feasibility Study on Commercialized FR Cycle Systems (FS), which carried out in last seven years. In the FS, the combination of the sodium-cooled FR with oxide fuel, the advanced aqueous reprocessing and the simplified pelletizing fuel fabrication was selected as the main concept which should be developed principally. A conceptual design study of the main concept and R&D of innovative technologies are implemented toward an important milestone at 2015. The development targets, which were set up at the beginning stage of FS, were revised for the FaCT project based on the results of FS and change in Japanese society environment and in the world situation. International collaboration is promoted to pursue fast reactor cycle technology which deserves the global standard and its efficient development.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Yoshida, Mitsunori; Okuda, Hiroyuki; Sato, Hiroyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.833 - 836, 2007/09
Breakdown of the cell voltage in the electro-electrodialysis process for concentrating HIx solution (HI-H O-I
O-I mixture) was preliminarily examined in an effort to clarify the optimal operation condition as well as to optimize the cell design for the application to the thermochemical water-splitting IS process for large-scale hydrogen production. Basic data such as electric resistance of HIx solution, overvoltage of the iodine-iodide ion redox reaction at graphite electrode, and the membrane voltage drop, were measured using HIx solution with composition of interest. Also, a methodology for estimating the cell voltage was discussed. The calculated cell voltage agreed well with the experimental one indicating the validity of the procedure adopted.
mixture) was preliminarily examined in an effort to clarify the optimal operation condition as well as to optimize the cell design for the application to the thermochemical water-splitting IS process for large-scale hydrogen production. Basic data such as electric resistance of HIx solution, overvoltage of the iodine-iodide ion redox reaction at graphite electrode, and the membrane voltage drop, were measured using HIx solution with composition of interest. Also, a methodology for estimating the cell voltage was discussed. The calculated cell voltage agreed well with the experimental one indicating the validity of the procedure adopted.
Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi; Iwanaga, Kohei; Kurata, Yuji; Sasa, Toshinobu; Oigawa, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.998 - 1007, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Oigawa, Hiroyuki; Nishihara, Kenji; Yokoo, Takeshi*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.434 - 442, 2007/09
In Japan, the partitioning and transmutation (PT) technology is being studied and developed to reduce the burden of the high-level radioactive waste (HLW) management. To demonstrate clearly the benefit of the PT technology on the waste management of future nuclear fuel cycles, the repository area necessitated to dispose of the HLW was discussed quantitatively for spent fuels from UO -LWR, MOX-LWR and MOX-FBR. Four options of separation process were assumed in the analysis: (1) Conventional PUREX reprocessing, (2) Transmutation of minor actinide (MA), (3) Partitioning of FP, and (4) PT for both MA and FP. The results showed that MA transmutation would be necessary to keep the emplacement area for MOX fuel at the same level as that for UO
-LWR, MOX-LWR and MOX-FBR. Four options of separation process were assumed in the analysis: (1) Conventional PUREX reprocessing, (2) Transmutation of minor actinide (MA), (3) Partitioning of FP, and (4) PT for both MA and FP. The results showed that MA transmutation would be necessary to keep the emplacement area for MOX fuel at the same level as that for UO fuel. The adoption of PT for both MA and FP was effective to further reduce the repository area independently on the fuel type, the reactor type and the cooling period.
fuel. The adoption of PT for both MA and FP was effective to further reduce the repository area independently on the fuel type, the reactor type and the cooling period.
Arai, Yasuo; Akabori, Mitsuo; Minato, Kazuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.980 - 988, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Okamura, Nobuo; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Ogino, Hideki; Kase, Takeshi; Koizumi, Tsutomu
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1070 - 1075, 2007/09
no abstracts in English
Aihara, Jun; Ueta, Shohei; Mozumi, Yasuhiro; Sato, Hiroyuki; Motohashi, Yoshinobu*; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.416 - 422, 2007/09
In high temperature gas-cooled reactors (HTGRs), coated particles are used as fuels. For upgrading HTGR technologies, present SiC coating layer which is used as the 3rd layer could be replaced with ZrC coating layer which have much higher temperature stability in addition to higher resistance to chemical attack by fission product palladium than the SiC coating layer. The ZrC layer could deform plastically at high temperatures. Therefore, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency modified an existing pressure vessel failure fraction calculation code to treat the plastic deformation of the 3rd layer in order to predict failure fraction of ZrC coated particle under irradiation. Finite element method is employed to calculate the stress in each coating layer. The pressure vessel failure fraction of the coated fuel particles under normal operating condition of GTHTR300C is calculated by the modified code. The failure fraction is evaluated as low as 3.5 10
10 .
.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Kubo, Shinji; Sakaba, Nariaki; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sano, Naoki; Nishihara, Tetsuo; Kunitomi, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.812 - 819, 2007/09
The objective of this study is to confirm the availability of proposed mitigation methodology against thermal load increase events initiated by the thermochemical water splitting IS process hydrogen production system coupling with the HTTR. JAEA has been performing the development of dynamic simulation code which can evaluate complex phenomena in the HTTR-IS system all at one once to achieve the requirement. The notable feature of the developed code is the APHX module which enables to estimate the IS process thermal load variation considering phase change and chemical reaction behavior assumed in the APHX. In this paper, two cases of dynamic calculation for the thermal load increase events were performed using the newly developed APHX module. The results of the analytical studies clearly show the availability of the developed model for dynamic simulation of the HTTR-IS system and the thermal load increase mitigation methodology.
Koyama, Shinichi; Ozawa, Masaki; Okada, Ken*; Kurosawa, Kiyoko*; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Fujii, Yasuhiko*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1530 - 1536, 2007/09
Simplified separation process was proposed based on ion-exchange technique. HCl, HNO and MeOH were used as an eluent. To develop an engineering scale concept, it is indispensable to establish the condition for safety operation. Corrosion test of structural materials in the HCl was performed by using some metals. In this experiment, it was proved that the Ta, Zr, Nb and hastelloy have good endurance to HCl solution. Research of thermal hazard of pyridine-type ion-exchange resin, MeOH and HNO
and MeOH were used as an eluent. To develop an engineering scale concept, it is indispensable to establish the condition for safety operation. Corrosion test of structural materials in the HCl was performed by using some metals. In this experiment, it was proved that the Ta, Zr, Nb and hastelloy have good endurance to HCl solution. Research of thermal hazard of pyridine-type ion-exchange resin, MeOH and HNO media system was studied in the view point of fire and explosion safety. There is no hazardous reaction between IER/MeOH, HNO
media system was studied in the view point of fire and explosion safety. There is no hazardous reaction between IER/MeOH, HNO media system. In the case of more than 150
media system. In the case of more than 150 C, we should pay attention to the exothermic reaction at dried condition NO
C, we should pay attention to the exothermic reaction at dried condition NO -IER or IER/HNO
-IER or IER/HNO media system.
media system.
Iwamura, Takamichi; Okubo, Tsutomu; Uchikawa, Sadao
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1718 - 1724, 2007/09
An advanced LWR concept of FLWR for TRU recycling has been investigated. The design study has shown the promising results for the feasibility of the concept, in conjunction with the investigated results obtained from the related R&D's for some key issues of FLWR development. In order to establish a robust nuclear energy supply system for the future, an appropriate combination of both the LWR and the FBR technologies, i.e. FLWR and Na-FBR, is considered to be preferable and realistic. This type of preferable combination is proposed in this paper.
Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Kato, Chiaki; Motooka, Takafumi; Ichikawa, Shiro*; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1389 - 1393, 2007/09
Authors were aimed for development of life evaluation method of components and clarification of corrosion mechanism of the components in nuclear reprocessing plant. Corrosion behavior of heat exchanger tubes in the reduced pressure evaporator made by ultra-low carbon type 304ULC stainless steel was studied. A simplified mock-up test apparatus was used for corrosion test with long-term test duration. Following results were obtained. The corrosion rates were increased from beginning of the test to more than 25,000 hours and then corrosion rate was reached to constant. From the measurement results of intergranular penetration depths, it was thought that intergranular corrosion was progressed on entire grain boundary around a grain and then the grain dropped out to the solution.
Sato, Takumi; Iwai, Takashi; Arai, Yasuo
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1090 - 1098, 2007/09
The electrolysis of burnup-simulated uranium nitride, UN, containing representative solid fission product elements (Mo, Pd, Nd) was investigated in the molten LiCl-KCl eutectic salt with 0.54 wt% UCl from the view point of application of pyrochemical reprocessing to nitride fuel cycle. It was found from cyclic voltammetry and anodic polarization curve measurement that anodic dissolution of UN began at about -0.75 V vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode in all samples. After the electrolysis at the constant anodic potential of -0.65
from the view point of application of pyrochemical reprocessing to nitride fuel cycle. It was found from cyclic voltammetry and anodic polarization curve measurement that anodic dissolution of UN began at about -0.75 V vs. Ag/AgCl reference electrode in all samples. After the electrolysis at the constant anodic potential of -0.65  -0.60 V vs. Ag/AgCl, most of UN was dissolved into LiCl-KCl as UCl
-0.60 V vs. Ag/AgCl, most of UN was dissolved into LiCl-KCl as UCl at the anode, and U was recovered in the liquid Cd cathode in all samples. Further, Nd was dissolved into LiCl-KCl as NdCl
at the anode, and U was recovered in the liquid Cd cathode in all samples. Further, Nd was dissolved into LiCl-KCl as NdCl , while Mo and Pd were not dissolved but remained at the anode.
, while Mo and Pd were not dissolved but remained at the anode.
Amamoto, Ippei; Kofuji, Hirohide; Myochin, Munetaka; Terai, Takayuki*
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.748 - 757, 2007/09
FP such as alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and rare-earth elements are apt to remain in the eutectic medium used in pyroreprocessing even after treatment at the pyrocontactor step. It is desirable to have the spent electrolyte purified for recycling which in turn, could lead to the reduction of HLW. This study is carried out to evaluate the feasibility of the electrolyte recycling process by the phosphate conversion technique. First of all, a reference block flow diagram, which consists of three steps, was designed based on known developmental results from literature. Subsequently, evaluation was undertaken by comparison with conventional relevant experimental and theoretical analysis results after gathering the essential basic data for thermodynamic calculation. The obtained computational value was then reflected to establish the preliminary conceptual flow diagram which would facilitate the next discussion and experiment for the realization of this process.
Washiya, Tadahiro; Komaki, Jun; Funasaka, Hideyuki
Proceedings of International Conference on Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycles and Systems (Global 2007) (CD-ROM), p.1467 - 1473, 2007/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing the new aqueous reprocessing system named "NEXT" (New Extraction system for TRU recovery), which provides many advantages as waste volume reduction, cost savings by advanced components and simplification of process operation. Advanced head-end systems in the "NEXT" process consist of fuel disassembly system, fuel shearing system and continuous dissolver system. We developed reliable fuel disassembly system with innovative procedure, and short-length shearing system and continuous dissolver system can be provided highly concentrated dissolution to adapt to the uranium crystallization process. We have carried out experimental studies, and fabrication of engineering-scale test devices to confirm the systems performance. In this paper, research and development of advanced head-end systems are described.